Protein 101
What is protein?
- Classified as a macronutrient, like carbohydrates and fats.
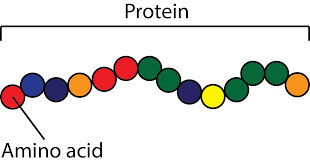
- It’s a complex molecule made up of chains of smaller units called amino acids.
- The specific sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique role.
- Found in virtually every cell of your body.
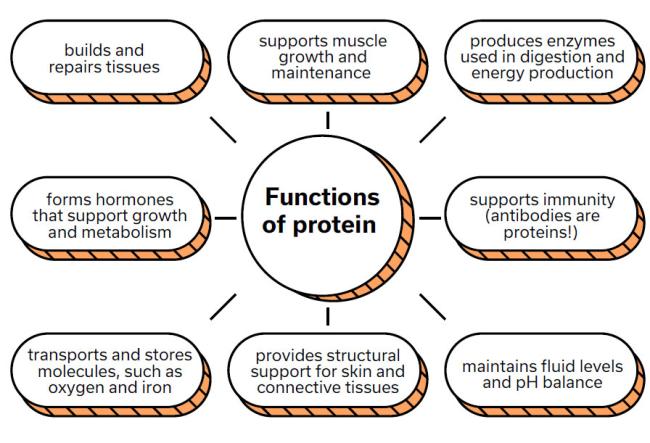
Why do we need protein?
How much protein do we need?
| Category | Protein intake (grams per pound of body weight) | Example for 150-poundperson (grams per day) |
|---|---|---|
| Average adults(sedentary) | 0.36 | 54 |
| Active adults (moderate exercise) | .05 - 0.7 | 75 - 105 |
| Athletes or bodybuilders | 0.7 - 1.0 | 105 - 150 |
| Older adults (50 or older) | 0.5 - 0.7 | 75 - 105 |
| Muscle maintenance during weight loss | 0.7 - 0.9 | 105 - 135 |
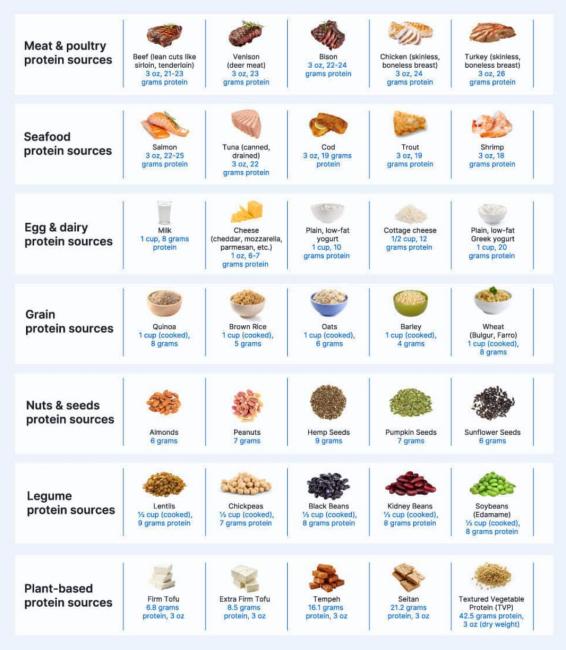
What are good food sources of protein?
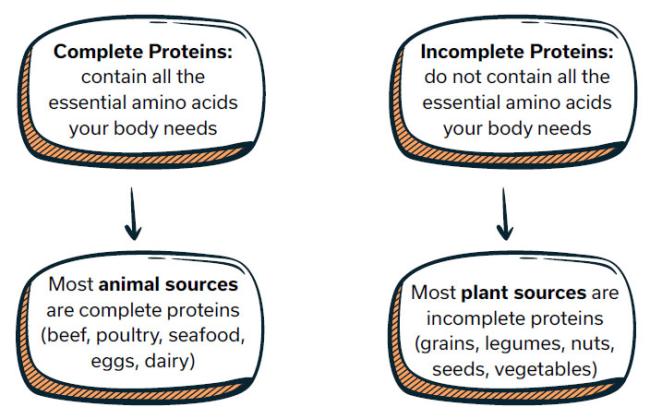
What are complete and incomplete proteins?
Essential amino acids are the ones your body cannot make and must obtain through food. If you are vegetarian or vegan, eat a variety of plant-based sources of protein to ensure you consume all the essential amino acids!
What about protein supplements?
- Most people don’t need a protein supplement.
- Prioritize protein from food first, but if you still struggle to get enough, consider a supplement.
- Whey protein (animal-based) and pea protein (plant-based) are both well-utilized by the body.
- When buying protein powders, look for unflavored versions to reduce exposure to unwanted ingredients (this also enhances its versatility!)
- Brands that sell unflavored versions include NOW, Naked, Designer Wellness and Garden of Life.
What else should I know about protein?
- Protein deficiency in this country is exceedingly rare.
- Your body can use about 25 to 30 grams of protein at a time for muscle synthesis.
- Protein intake alone will not build muscle - it must be paired with an appropriate exercise routine.
- Protein intake up to 1.0 gram per pound of body weight is generally safe for healthy adults.
- If you have kidney issues, consult a healthcare provider before increasing protein intake.